Install and Get Started: RAG and Context Engineering
There are two ways to get started with RapidFire AI for RAG/Context Engineering:
Google Colab - Zero local setup, takes under 2 minutes to get started. However, this option has limitations due to the free T4 GPU instance, viz., it works only for smaller models and small datasets.
Full Installation - Complete setup with full functionality for any environment (local machine or cloud machine), supporting models and datasets of any size, as well as your own OpenAI keys.
Choose the option that best fits your needs below.
Google Colab
Try RapidFire AI RAG instantly in your browser with our pre-configured Google Colab notebook. No installation required.
Launch the notebook: RapidFire AI RAG on Google Colab
Note
The Google Colab environment is limited to small models and datasets due to their free resource constraints.
Full Installation
To install RapidFire AI for RAG/context engineering on your local machine or remote/cloud instance for complete functionality without limitations, follow the steps below.
Note that if you plan to use only OpenAI APIs and not self-hosted models (for embedding or generation), you do NOT need GPUs on your machine. But you must provide a valid OpenAI API key via a config argument as shown in the GSM8K and SciFact tutorial notebooks.
Step 1: Install dependencies and package
Obtain the RapidFire AI OSS package from pypi (includes all dependencies) and ensure it is installed correctly.
Important
Requires Python 3.12+. Ensure that python3 resolves to Python 3.12 before creating the venv.
python3 --version # must be 3.12.x
python3 -m venv .venv
source .venv/bin/activate
pip install rapidfireai
rapidfireai --version
# Verify it prints the following:
# RapidFire AI 0..14.0
# Due to current issue: https://github.com/huggingface/xet-core/issues/527
pip uninstall -y hf-xet
The tutorial notebooks for RAG evals do not use any gated models from Hugging Face. If you want to access gated models, provide your Hugging Face account token. For more details on that, see Step 1 here.
Step 2: Initialize RapidFire AI
Run the following command to initialize rapidfireai to use the correct dependencies for RAG evals:
rapidfireai init --evals
# It will install specific dependencies and initialize rapidfireai for RAG evals
Note
You need to run init only once for a new venv or when switching GPU(s) on your machine. You do NOT need to run it after a reboot or for a new terminal tab.
Step 3: Open the tutorial notebooks
After completing Step 2, open one of the tutorial notebooks via Jupyter, say the the FiQA RAG Q&A chabtot use case (more here: Example Use Case Tutorials). Use the following command to start the jupyter server to avoid connection issues. Open the URL provided by this command via your browser.
jupyter notebook --no-browser --port=8850 --ServerApp.allow_origin='*'
Important
As of this writing, the IC Ops panel on the notebook will work only with jupyter as above. We will expand support for more IDEs soon.
You can see the files under the “tutorial_notebooks” folder in the directory where you initialized rapidfireai.
FiQA: RAG for Financial Opinion Q&A Chatbot: View on GitHub
GSM8K: Context Engineering for Math Reasoning: View on GitHub
SciFact: RAG for Scientific Claim Verification: View on GitHub
Step 3b (optional): Forward ports if using remote machine
If you installed rapidfireai on a remote machine (e.g., on a public cloud) accessed via ssh and opened the notebook there, you also need to forward the following two ports on your client machine. Run the following ssh commands with your correct username and remote machine IP. (Or forward these ports via your VSCode or other IDEs.)
ssh -L 8850:localhost:8850 username@remote-machine
ssh -L 8851:localhost:8851 username@remote-machine
Quickstart Video (3.5min)
Full Usage Walkthrough Video (13.5min)
Step 4: Run the notebook cells
Run the cells one by one as shown in the above videos. Wait for a cell to finish before running the next.
Imports
Load datasets
Create named RF experiment
Define RF RAG spec that wraps LangChain classes
Define data preprocessing and post processing functions
Define eval metrics functions per batch and for accumulation
Define RF generator spec that wraps vLLM or OpenAI classes
Define rest of multi-config knob dictionary and generate config group
Launch multi-config evals; adjust
num_shardsas per desired concurrency (see Run Evals for details)
Step 5: Monitor online aggregation of eval metrics on in-notebook table
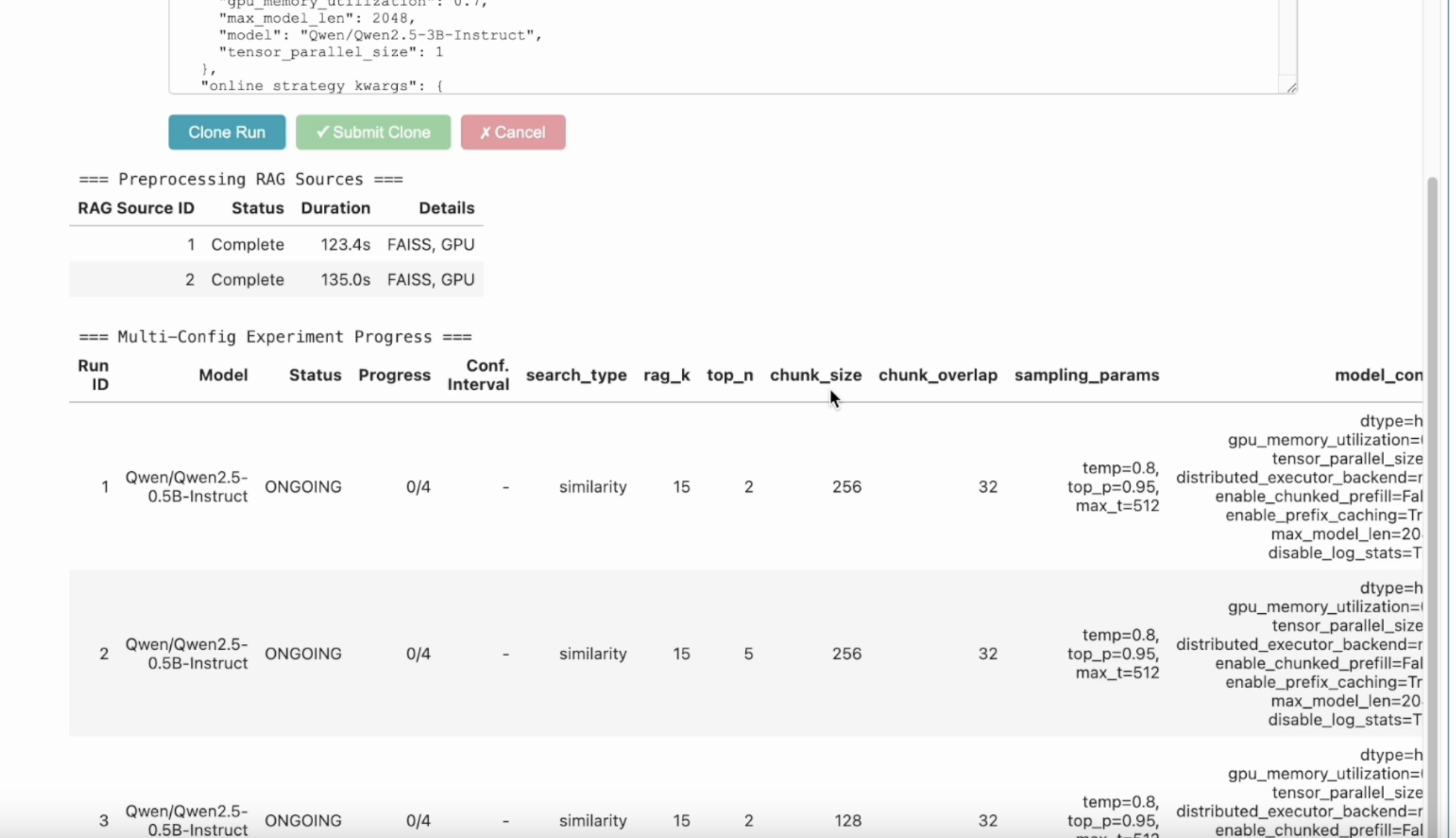
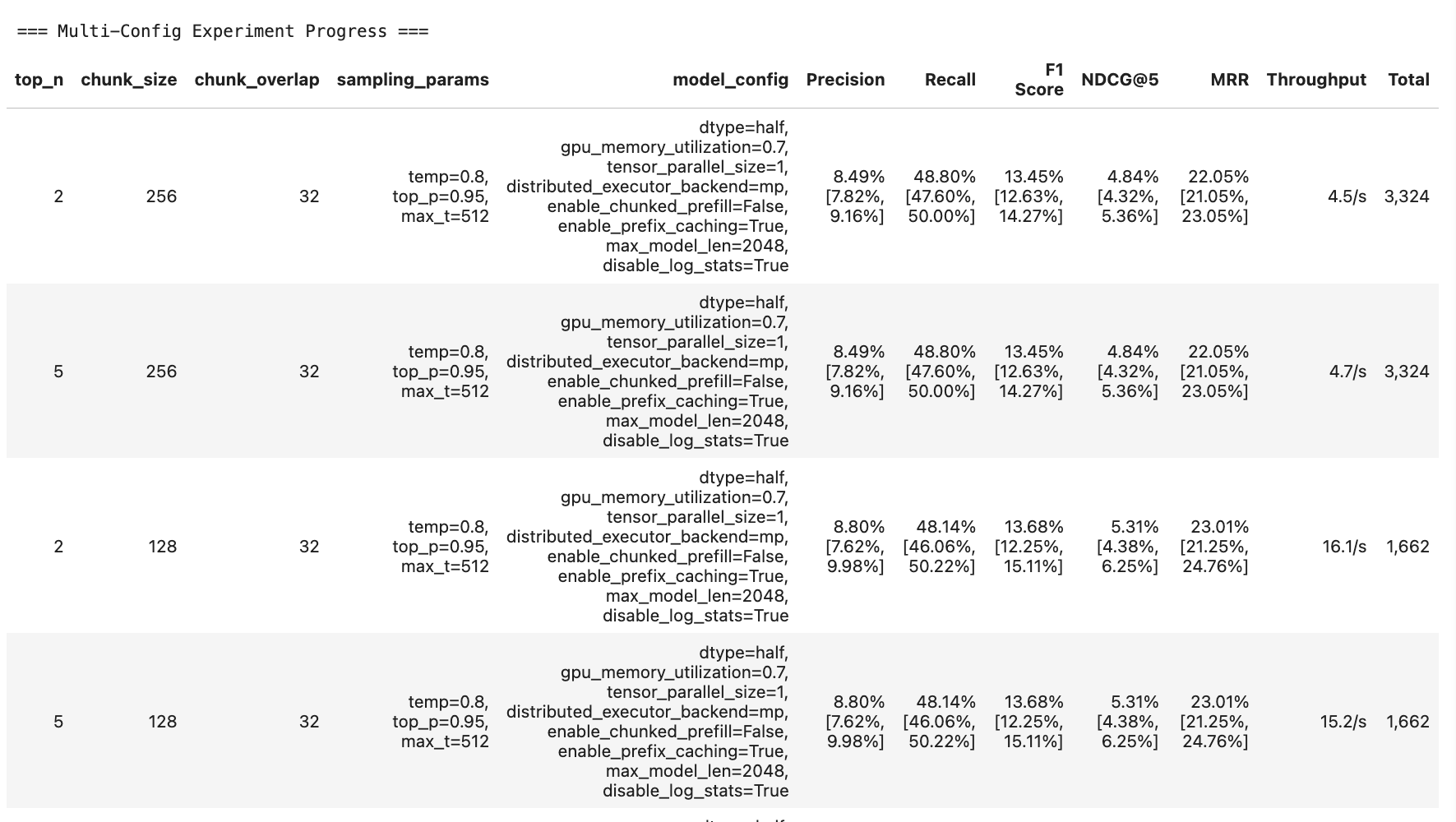
Step 6: Interactive Control (IC) Ops: Stop, Clone-Modify; check their results
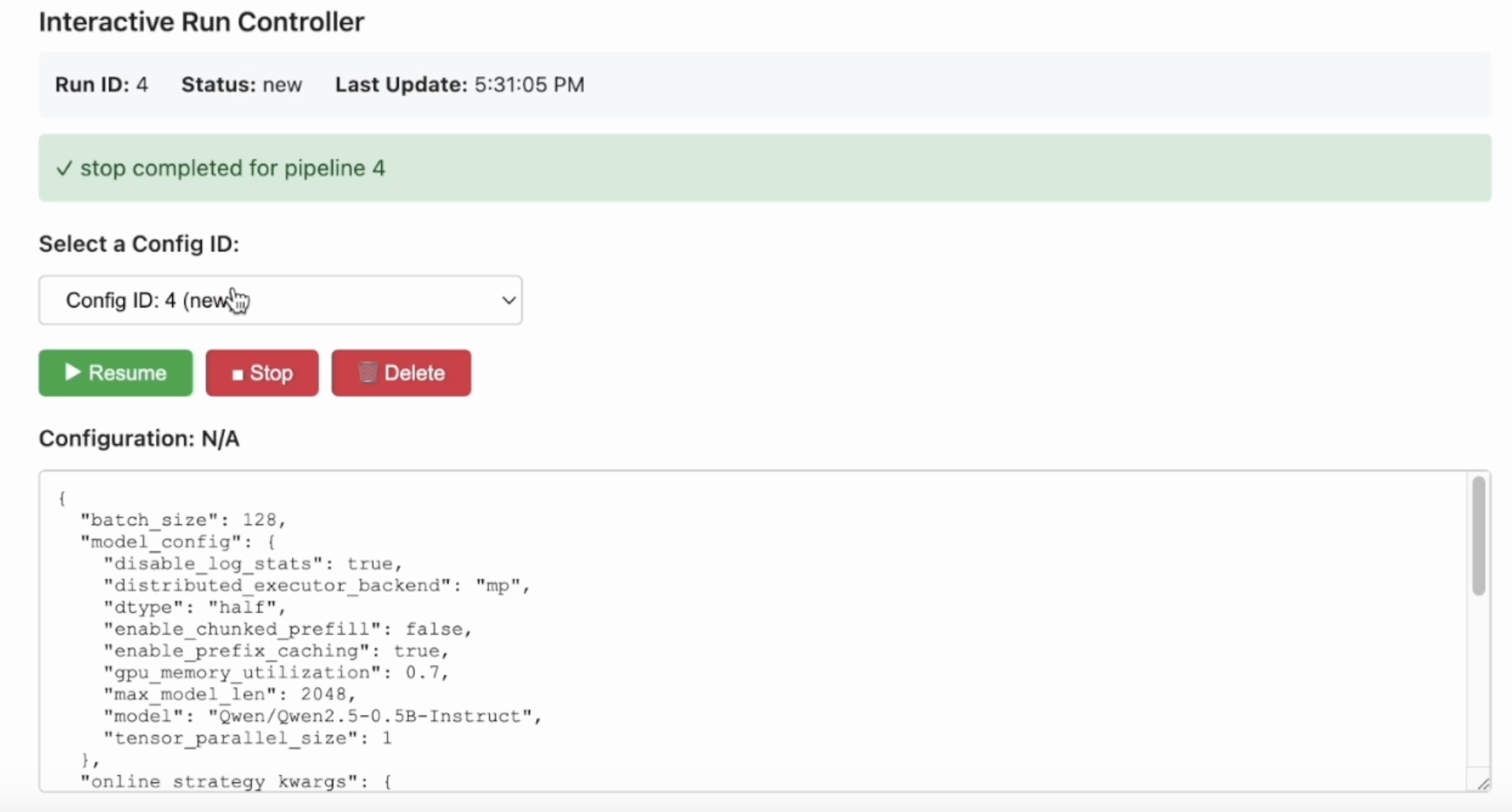
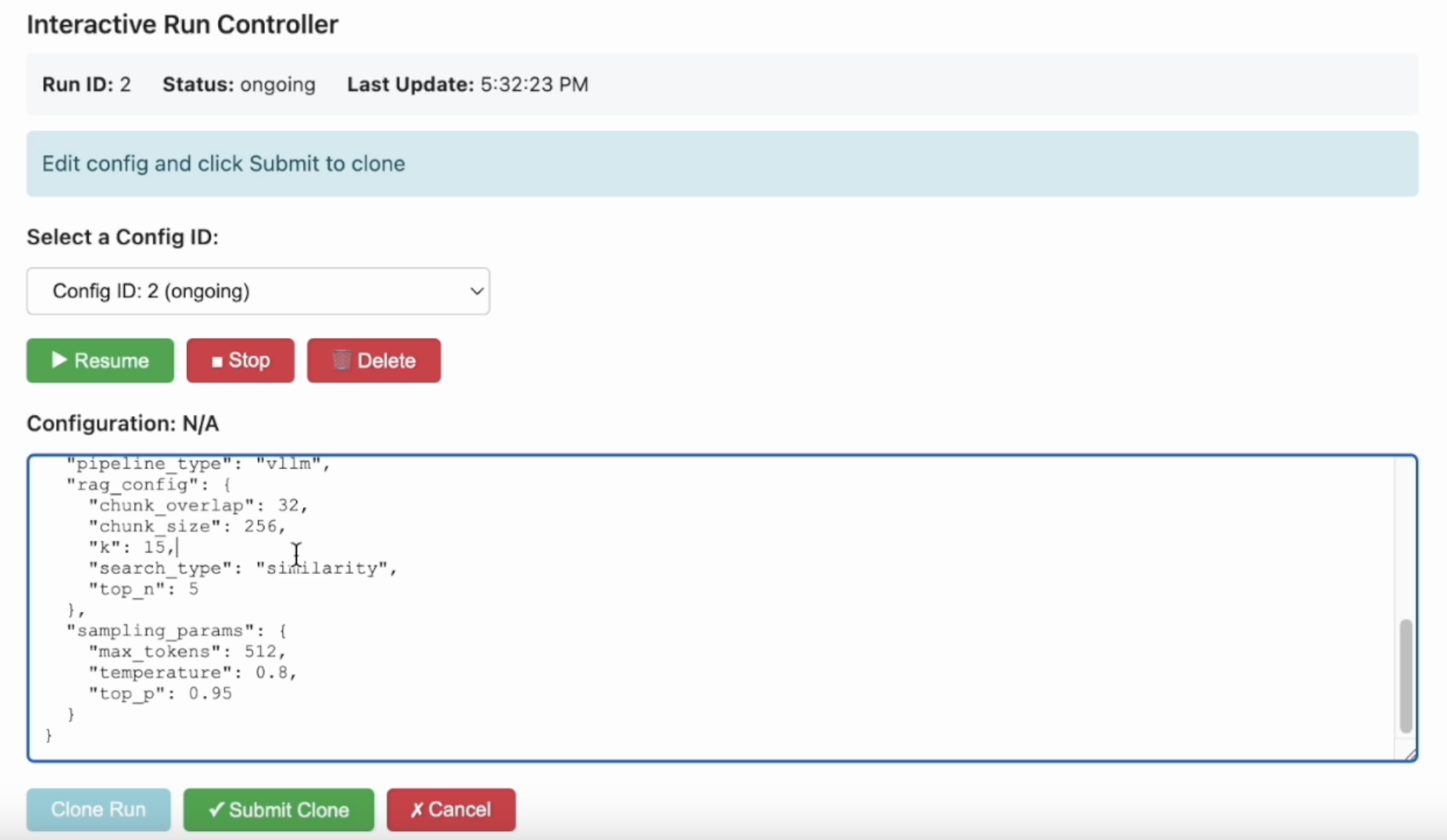
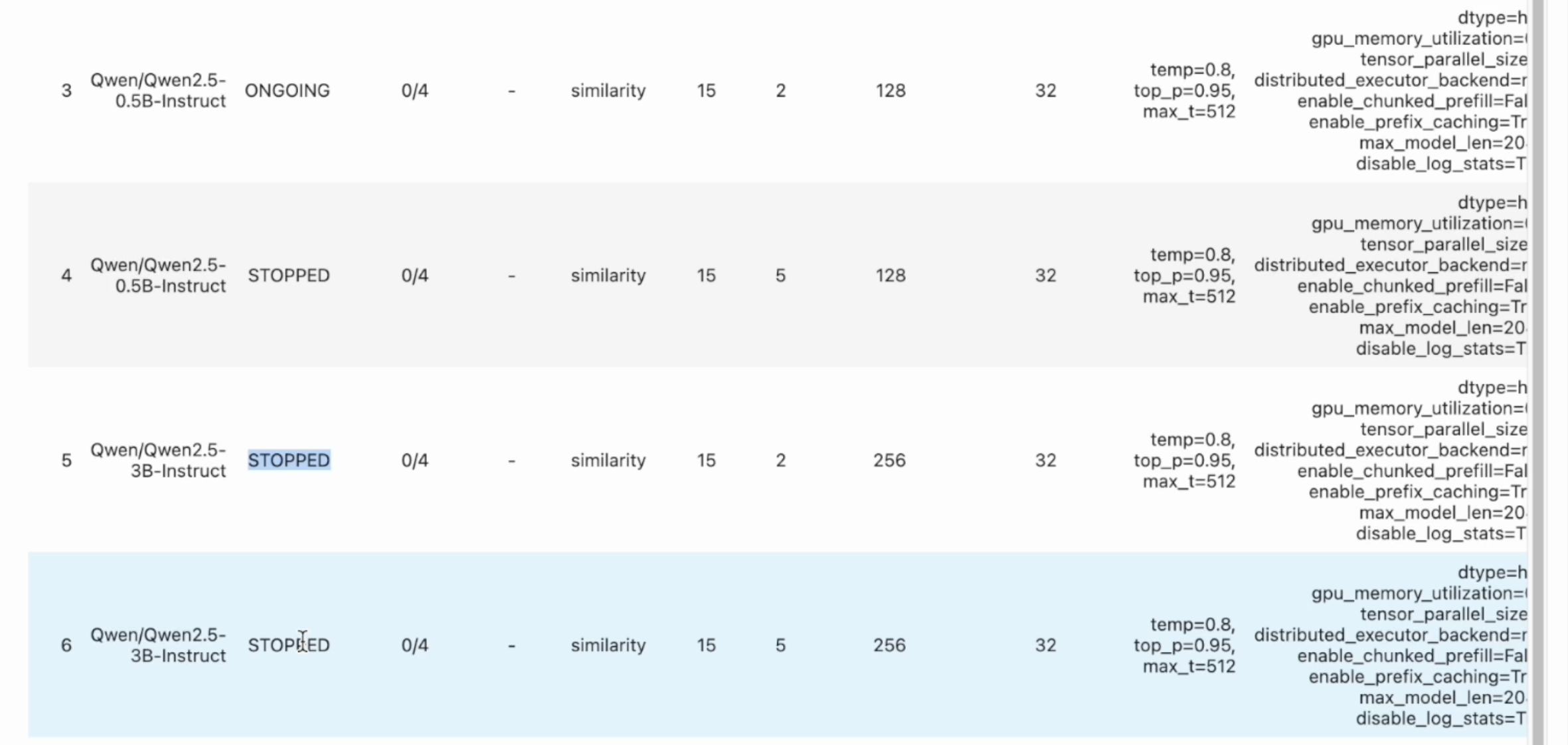
Step 7: Inspect results, end experiment, and check logs.
Run the cell to print some entries of the evals results. End the expeirment after you are done with it.
You can then move on to another (named) experiment in the same session.
Run as many experiments as you like; each will have its metrics apppear on its own table under the run_evals() cell.
All experiment artifacts (metrics files, logs, checkpoints, etc.) are persistent on
your machine in the experiments path specified in the constructor.
When you are done overall, just close the notebook. RapidFire AI for evals does not maintain any running server processes.
Step 8: Venture Beyond!
After trying out the tutorial notebooks, explore the rest of this docs website, especially the API pages for RAG and context engineering. Play around more with IC Ops and/or run more experiments as you wish, including changing the prompt schemes, generator models and its knobs, chunking / reranking / retrieval knobs, and eval metrics definitions.
You are now up to speed! Enjoy the power of rapid AI customization with RapidFire AI!